Nov 28, 2019
What is the SILKYPIX?
The SILKYPIX series is a digital processing software that provides powerful support of RAW data and JPEG data. How high-definition image can be obtained using the powerful computing power of a personal computer? Digital cameras, which were previously thought to have no way of doing so, have unique disadvantages, such as:
- Unnatural edges at high saturation color boundary
- False color on the fine structure part
- Noise in high-sensitivity shooting
It thoroughly suppresses the use of such functions, ensuring both high resolution and high color separation performance. The goal is a smooth, natural image like silk. The origin of the name of the SILKYPIX is there.
High resolution
– Achieve higher resolution –
It is generally recognized that resolution is determined by the number of pixels in the lens and image sensor. In practice, however, the process of demosaicing during the development process is a big key. In other words, you can obtain higher resolution by shooting with RAW data and developing with the SILKYPIX series.
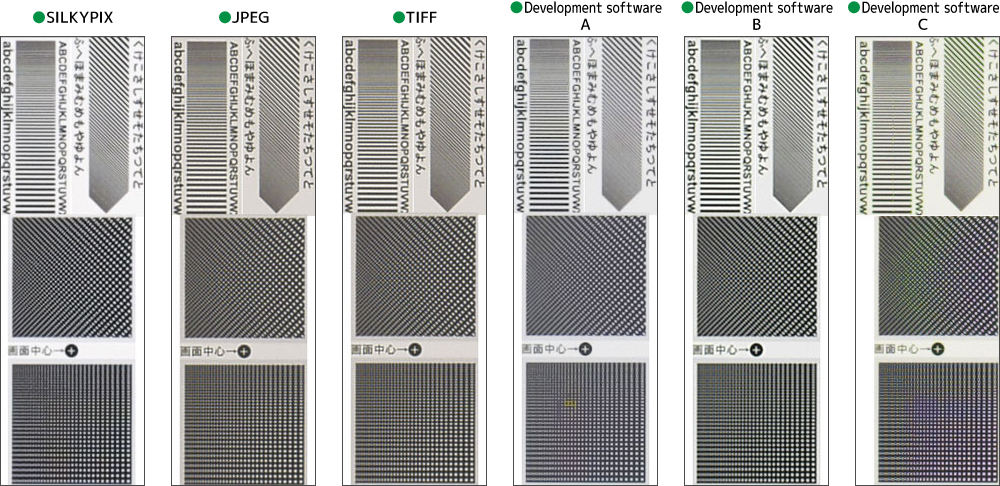
High color separation performance
– Equipped with a proprietary demosaic logic system –
Digital cameras have a special effect on highly saturated color boundaries, where the edges are dropped and a white false edge is created. This is the reason why it is said to be a digital picture. This happens because the color resolution (hue) is lower than the brightness resolution.
In SILKYPIX, colors are separated well, and there are few jagged, false edges, and false colors at the high saturation border. Whites and blacks can be represented well, but dark borders can be blurred as if they were too focused, become jagged, or have white or black, neutral areas of the border. In the prior art, the poor separation of colors caused a number of poor phenomena that dirty the image. The SILKYPIX series features an entirely new type of demosaic logic to improve color resolution, providing a high-level color resolution.
Cyan-yellow boundary separation
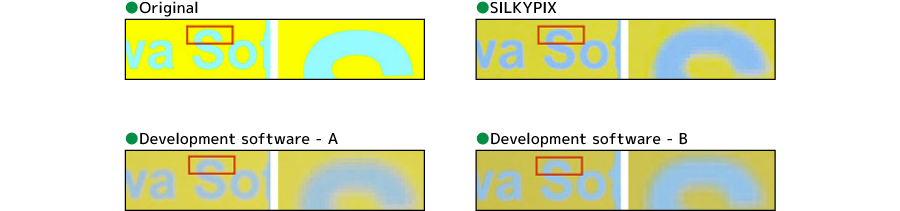
- SILKYPIX: It can be seen that even the difficult cyan and yellow borders are cleanly separated at high resolutions.
- Development software – A: You will notice that the outlines are blurred and that the resolution is not sufficient.
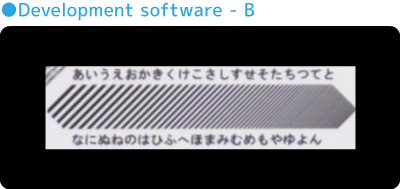
- Development software – B: You can see that the outline is black and the color separation is not working properly.
Red-blue boundary separation
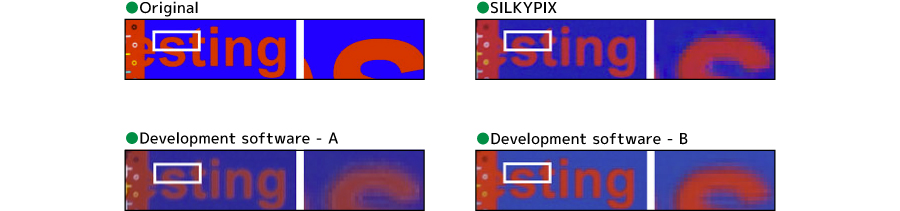
- SILKYPIX: Even the hard-to-do boundary between blue and red has been decomposed at a high level.
- Development software – A: The red area is discolored, and the separation is not performed properly.
- Development software – B: The red is a little vermilion, and the blue part of the border is dark.
Magenta-green boundary separation
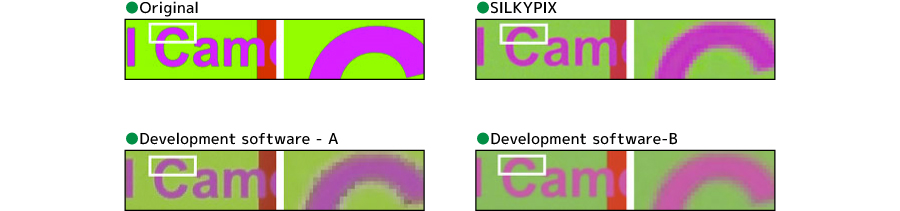
- SILKYPIX: Both magenta and green were clearly separated, showing good color development.
- Development software – A: Many corners appear in the outline, and a blackish color is added to the outline.
- Development software – B: The curve in the upper left of C is outside the outline. In addition, the overall saturation is reduced.
Ideal frequency response
– Ideal characteristics for all frequencies –
The SILKYPIX is ideally suited for all frequencies up to the critical resolution. Simply raising the limit resolution does not produce good image unless a high linear decomposition is achieved in various spatial frequency regions up to that. SILKYPIX is successful in ensuring unparalleled performance not only at full resolution, but also at all frequencies. This also suppresses the moire-like ugly phenomena.
Spatial frequency response characteristics
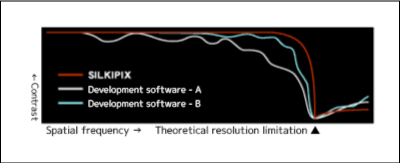

Almost all resolution charts with different spatial frequencies have little observed false colors or moire occurrences. So we can see that it has flat characteristics in the continuous spatial frequency plane.

From the low frequency range, we can see that all the false colors are generated.
Although the resolution in the high frequency range is achieved, false colors still occur.
Low false color
– Advanced pixel value prediction logic –
Most digital cameras today have an image sensor with a structure called a Bayer array to obtain color images. Rather than sampling R, G, and B, which are the three primary colors of light at the same time, one sensor samples only one of the colors. By arranging the RGB sensors in order, a color image is obtained as a whole.
By their nature, this Bayer array is colored at the edges and in the fine structures. This is known as false color. The false color occurs mainly around the image due to lens aberrations. In addition, the false color occurs because the focus is distributed forward and backward on the axis of focus due to the difference in the index of refraction, also it causes a folding error at high spatial frequency. The false colors can be caused by a variety of causes, including the leakage of charge from the image sensor.
In the SILKYPIX series, this false color is suppressed at higher levels with advanced pixel-value prediction logic. In fact, high resolution and low false color conflict, and achieving high resolution results in more false colors, while suppressing false colors results in a decrease in resolution. The SILKYPIX series makes both very high-level compatibility.
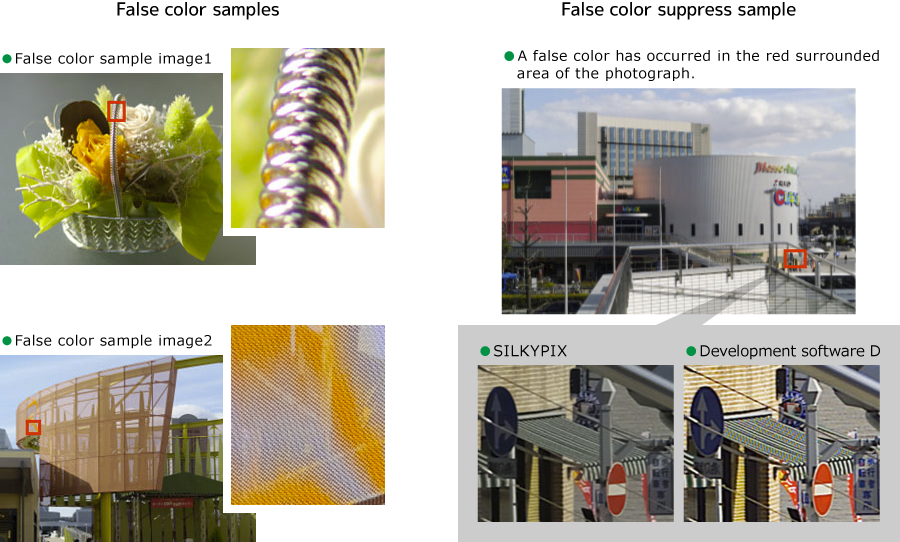

Improvement of S/N during high-sensitivity shooting
– Surprisingly clean images in high-sensitivity shooting –
S/N is the balance between resolution and noise level. The effects and resolution of noise reduction are trade-offs. If you shoot a dark subject at high sensitivity, the noise in the image sensor can introduce color noise inherent in digital cameras. This is very bad for humans. Many photographers don’t like this, and they give up on high-sensitivity shooting.
The SILKYPIX series has a function to reduce the color noise, and it can produce surprisingly clean images even in high-sensitivity shooting. This will extend the range of shooting methods and subjects, allowing you to create new pictures.
Comparison of color noise during high-sensitivity shooting

Reduce highlight hue deviation
– Reduce hue drift at a high level –
This feature suppresses the effect of hue rotation in the highlights. For example, in a portrait image, if the exposure is raised before the skin is highlighted, the highlight border from the skin tone to the white is likely to become yellow. In the SILKYPIX series, this hue deviation is suppressed at high levels for natural highlights reproduction.
Faithful color reproduction and a color mode tailored to the subject
– Equipped with unique color matching logic –
SILKYPIX has its own color matching logic that uses several color matching data from a number of test footage to ensure accurate color reproduction under various light sources. Highly accurate color matching is possible for light sources with various spectrum distributions, such as fluorescent lights, light bulbs, ragtones, strobe light, and mixed light. This eliminates very little bad light source that degrades color fidelity.
With SILKYPIX, you can produce straightforward, highly saturated, linear image without creating your own colors. In addition, there are two other mode settings, called color mode, that determine the direction of color reproduction.
Colors don’t always produce “good” image of faithful color reproduction only. We know that the color that remains in our memory, or the color that we want this object to be in, is out of place. When remembered or expected colors are reproduced as image, they look like “good-colored image”.
The “memory color” mode takes advantage of these characteristics to create colors according to the memory color and expected color trends. It also has a “Beautiful flesh tone” mode, which makes it difficult to reproduce a person’s skin beauty with memory colors. This is to make the color centered on the actual skin tone as close as possible to “good skin tone” and to balance with the nearest color, so the overall saturation is reduced and the expression is high lightness except for the color far away from the skin tone. With SILKYPIX, you can use these color modes to achieve color reproduction suitable for landscapes, people, and so on.

 Go Back
Go Back
